Magnetic surveys

Zhanazhol Munai Service LLP performs magnetic exploration using the best equipment in the industry, which allows obtaining the highest quality data.
The difference between this method and other geophysical surveys is high productivity. The search and exploration of iron ore is very effective, the speed of geological mapping, structural studies, and the search for minerals of various types is increasing.
Magnetic survey is the most important and widely used geophysical method of achieving geophysical exploration objectives. The basis of the method is the study of the Earth's magnetic field. Our planet, being a cosmic body with a certain internal structure, generates a constant magnetic field. It is called "normal" or "primary".
Most of the rocks and ore have a magnetic property and are magnetized under the influence of the Earth's field, creating abnormal (secondary) magnetic fields. By means of magnetic exploration, it is possible to identify such anomalous fields against the background of the observed or total geomagnetic field, as well as to carry out a geological interpretation of the data obtained.

- Ground—based magnetic exploration is necessary for detailing anomalies and mapping, where the highest accuracy is required.
Tasks to be solved:
- mapping and prospecting - used in large scale geological mapping with a scale of 1:50000 - 1:10000 and in the direct search for iron ore or other minerals;
- prospecting and exploration, detailed with a scale of 1:10000 and larger — help to identify ore bodies on the territory, assess their size, shape, degree of magnetization and position in the rock.

- Aeromagnetic exploration is a very fast and productive method, thanks to which it is widely used when it is necessary to study magnetic fields on large objects — land, water areas.
Tasks to be solved:
- regional on a scale of 1:200,000 and smaller — conducted if necessary to study the deep geological structure of land or water areas on a large territory;
- mapping — allows you to assess the prospects of the studied area for the amount of iron ore or other minerals contained in them; scale — 1:100000 - 1:50000.
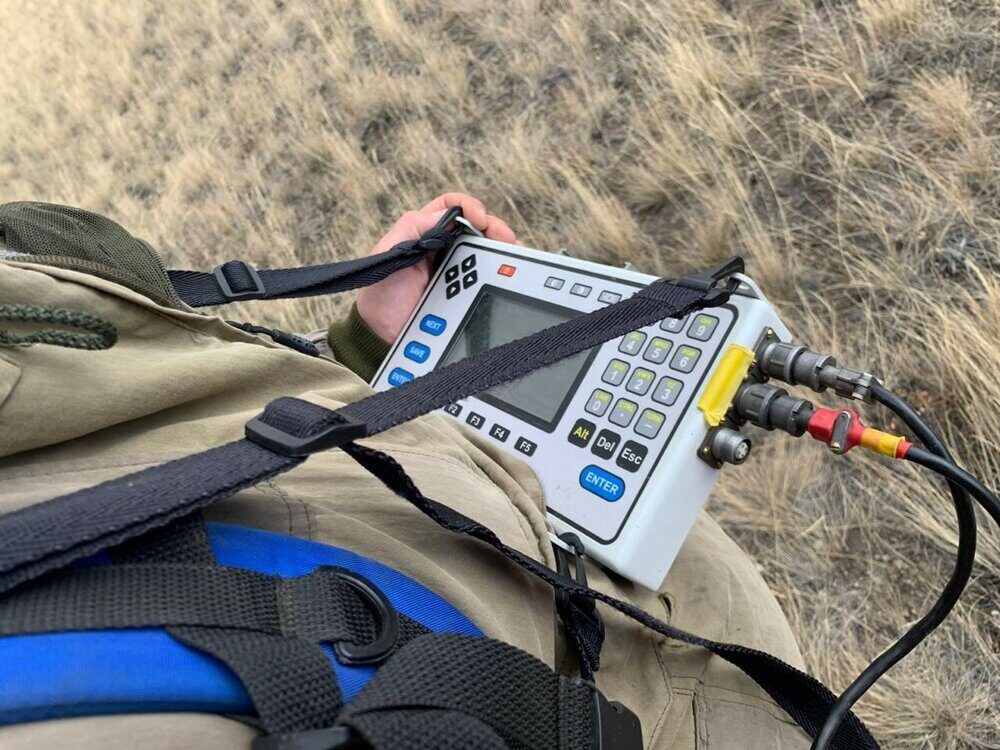
The technique of ground-based magnetic exploration involves the use of specific equipment. One of the most effective is the MMPOS 1 magnetometer and the G-859SX cesium magnetometer from the manufacturer Geometrics (USA).
- G-859SX is installed in low-gradient fields near the work site, used as a magnetovariation station that allows monitoring the quality of work;
- MMPOS-1 is operated in case of need for land survey, in the process of movement.
In order to monitor the stability of the instruments, readings are taken from them before the start of the study and at the end of the run. It is possible to control the quality of the results obtained by setting up independent control observations. Their volume does not exceed 5% of the total number of points; data are checked upon completion of field work. The results of control observations allow us to determine the average quadratic error that occurred in the observations of the main instruments.

The new cesium magnetometric system allows you to obtain the highest quality raw data — 0.020 nT/√Hz RMS. Currently, it is the best tool in its segment for measuring the total magnetic field strength. Its creation was based on the standard industrial model G-858 MagMapper, which was a reliable research module with proven performance characteristics.
An integral part of the module is the NovatelTM GPS unit equipped with the WAAS/EGNOS/MSAS function. It opens up the following possibilities:
- conducting research on large areas with high measurement density;
- registration of magnetometric data and receipt of GPS information with a frequency of up to 5 samples per second;
- prepare a digital record of the received data in compressed form and record them in high-capacity RAM with subsequent transfer to a computer for permanent storage and processing.
Another convenience of the Geometrics G-859SX magnetometer is the possibility for the user to choose parameters such as sensitivity, resolution, and data logging efficiency. Additionally, it is possible to adjust the coordinates of the survey profile system on the map, adjust the GPS location information.
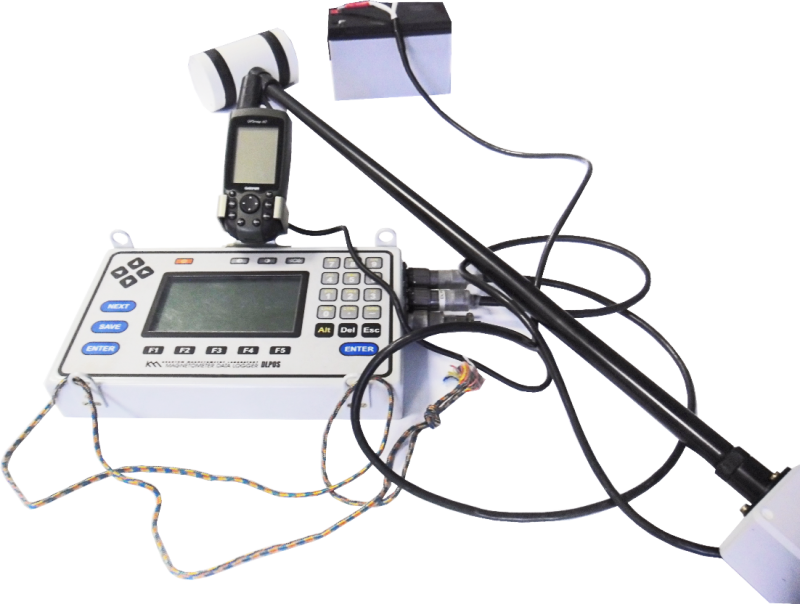

High-precision instrument based on the Overhauser effect. The main purpose is to measure the geomagnetic field module. Work opportunities — in the process of land survey or as a stationary variation station. The main features are the connection of GPS receiver for coordinate reference of measurements on the ground. This function is available thanks to the magnetometer control unit.
4 modes for the production of field work:
- areal survey with semi-automatic input of picket and route;
- pedestrian survey, in which coordinates and time are entered automatically by GPS receiver;
- continuous measurements are cyclical and the duration of each cycle is 1 or more seconds; GPS—binding is allowed;
- in the form of a base station (variation).
DLLink software is attached to the device, which provides data transfer to the user's computer. The POSManager program allows you to obtain graphical and textual visualization of variational and route measurements. This data is convenient for monitoring, editing and saving.
Aeromagnetic survey is performed by the MagArrow flight magnetometer, the DJI Matrice 600 Pro carrier UAV and the G-859SX cesium magnetometer. The G-859SX magnetometer is installed in a low-gradient field in the area of the work site for use as a magnetovariation station for quality control, while the MagArrow magnetometer on the DJI Matrice 600 Pro UAV carrier is used for in-flight survey.
In the integrated MagArrow+DJI Matrice 600 Pro device, the high-precision MagArrow sensor element is towed on a cable cable from the DJI Matrice 600 Pro unmanned aerial vehicle. This makes it possible to exclude the influence of the magnetic field of the carrier on the reading of the device.
To control the stability of the devices, a network of reference routes is created, along which readings are taken at the beginning and at the end of the working day. The quality control of the magnetic work carried out is carried out by setting up independent control observations carried out in the amount of 5% of the total length of the routes traveled upon completion of field work.
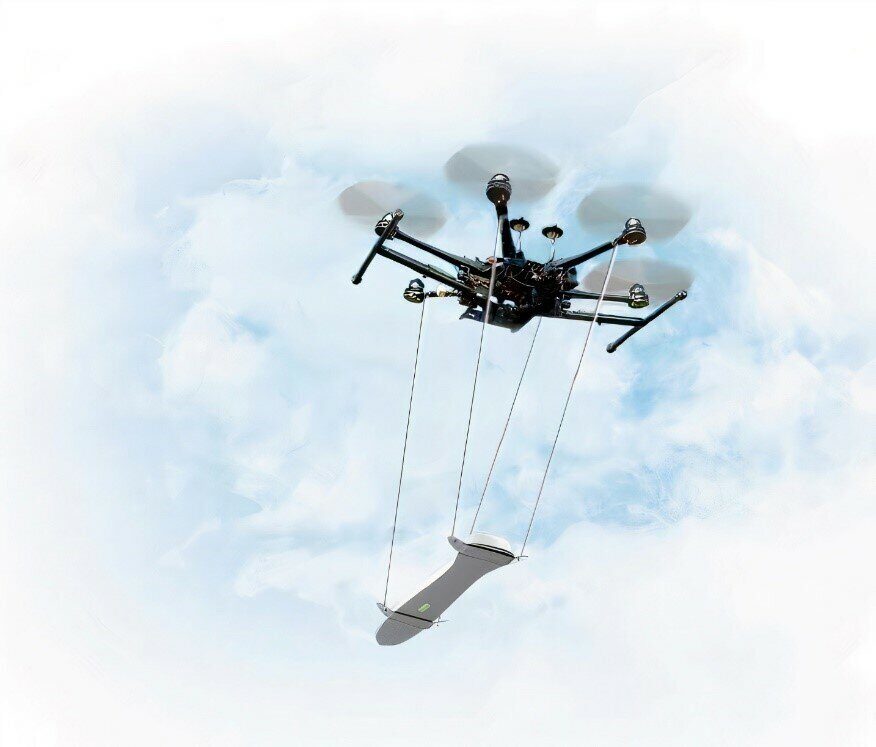

MagArrow is used as a magnetometer, which was designed specifically for use on drones. It is a lightweight and compact system with high performance and versatility, allowing you to conduct aeromagnetic surveys from any type of light aircraft with an average payload.
The electronics are packaged in a fully autonomous system, which consists of:
- data collection devices;
- two internal miniature MFAM magnetometers;
- GPS unit, IMU sensor and lithium polymer battery.
All this is integrated into a small aerodynamic capsule that weighs one kilogram (2.2 lbs.) and has a length of 1 meter (3.281 feet). The sampling frequency of 1000 Hz is synchronized with the built-in GPS, which allows the system to work independently of the UAV. With such a high sampling rate, the device can take surveys every 1 cm of the route segment at a given speed of 10 m/s.
- igneous with high magnetic susceptibility: ultrabasic, basic rocks, weakly magnetic or moderately magnetic acidic rocks;
- metamorphic have, as a rule, low parameters compared to igneous;
- sedimentary rocks are non magnetic, but there are exceptions in this category - these are some types of sandstone and clay;
the rocks that make up the geological structure of the Earth are located among the host rocks and for this reason they do not measure the absolute value of the parameters of the studied structure, but only their changes (in other words, the effective magnetic susceptibility is measured, estimated by the formula: δχ= xstr χ0, where by χ0 should be understood the magnetic susceptibility of the host rocks).
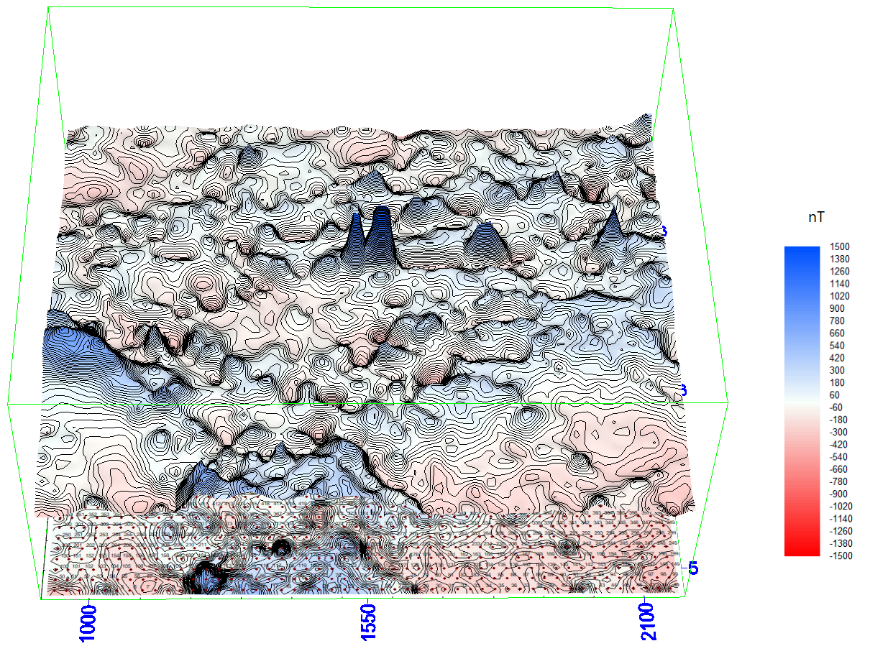
The value of δχ can be positive and negative, vary in a fairly wide range, but it is never equal to zero. And it is thanks to this that magnetic anomalies appear, recorded by sensitive equipment. The value of δχ depends on the existing geological situation.
Ferromagnets and the rocks they are part of are leaders among substances that create anomalies in magnetic fields. Since the magnetic susceptibility of a rock can vary millions of times, which is a fairly high limit of indicators, the intensity of anomalies also changes with it, varying in the range from a fraction to hundreds of thousands of nanotesla. To register such a field, it is necessary to use specialized highly sensitive devices capable of operating in a wide dynamic measurement range.
The method of magnetic exploration and gravity exploration is a set of measures that include the selection of the optimal method for research and instruments for conducting surveys, as well as observation systems, error calculations and the form of preparation of results. The main purpose of the technique is to obtain a conditioned material, on the basis of which it is possible to judge the location of anomalies in the magnetic field of the selected area of the territory and perform geological tasks.
Interpretation of the results of magnetic exploration
Interpretation of the received data includes geophysical interpretation and geological interpretation. These 2 studies are closely related.
Stages of work execution:
- Interpretation of magnetic field anomalies. The morphology of the results makes it possible to determine the location of structural or geological elements on the terrain plan, as well as to establish their nature, knowing the magnetic properties of the rock and its geological and structural architecture.
Quantitative interpretation or solution of the inverse problem of magnetic exploration. The task of this stage is to determine the quantitative parameter of the object under study.
Geological interpretation of magnetic anomaly is similar to gravity exploration.
Qualitative interpretation allows you to detect:
- региональные крупные по размеру аномалии, которые связаны со структурно-тектоническим строением проверяемого района;
- локальные аномалии, приуроченные к местам нахождения магнитных руд и отдельных слоев, имеющих высокие магнитные свойства.
Quantitative (calculated) interpretation is aimed at:
- determination of the depth and size, the exact location of the mineral;
- calculation of the angle of incidence of the geological body that created the magnetic anomaly.
By means of the obtained data, the inverse problem of magnetic exploration is solved.
A well-thought-out range of activities, including magnetic exploration, gravity exploration and other geophysical methods selected for the geological and geophysical feature of the area being checked, allows accurate and reliable geological interpretation of the data obtained.
Magnetic exploration in combination with seismic and gravity exploration is used to conduct geotectonic zoning — mapping of various regional structures:
- anticlinorium and synclinorium;
- intermountain troughs, fault zones;
- vaults and vugs of the crystal foundation.
Magnetic exploration also contributes to the assessment of the physical properties, structure and composition of rock, mapping of oil and gas-bearing objects and areas of salt dome tectonics.
Aeromagnetic exploration is used when it is necessary to conduct small- or medium-scale geological mapping. By means of ground-based magnetic observations, mapping, exploration and prospecting surveys are carried out. Focusing on the maps of anomalies in the geomagnetic field of the studied area, it is possible to determine the shape, location of the rock and its magnetic properties. Sedimentary and igneous rocks under sediments, deep faults give the clearest signals. This is due to the presence of magnetic rocks, large-sized iron ore deposits, intrusions of various compositions, and effusive complexes. The data from the surveys are necessary as the basis for the rational formulation of prospecting and geological survey work.

This task is best solved by magnetic exploration. The study is carried out in several stages:
- Aeromagnetic survey — helps to detect anomalies that intensively form iron ore deposits. The intensity of anomalies is often estimated in hundreds and thousands of nanotesla.
- Ground survey. Its task is to detail anomalies detected during aeromagnetic survey. Both qualitative and quantitative interpretation of the results is carried out.
Magnetite ores are much easier to detect than hematite deposits, as they are surrounded by more intense anomalies.
Magnetic exploration gives excellent results in the search for the following minerals:
- polymetallic sulphide, manganese and copper-nickel deposits;
- manganese ores, platinum, molybdenum, bauxite, placer gold deposits, etc.
Republic of Kazakhstan, Aktobe, Tauelsizdik ave., 5 k. 1, office 45




